The application of computednanotomography in biomedical sciencesand medicine
Uporaba nanotomografijev biomedicinski znanosti in medicini
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18690/actabiomed.285Ključne besede:
računalniška tomografija, CT, mikrotomografija, mikro-CT, nanotomografija, nano-CT, biomedicinsko slikanjePovzetek
Namen: Računalniška nanotomografija (nano-CT) je napredna slikovna tehnika, ki omogoča visoko ločljivo tridimenzionalno (3D) vizualizacijo na celični in subcelični ravni, ter tako bistveno presega zmogljivosti tradicionalnih tehnik računalniške tomografije (CT) in drugih slikovnih metod. Ta pregledni članek obravnava tehnološke novosti nano-CT, njegove trenutne zmogljivosti in potencialno vključitev v klinično medicino.
Metode: Izvedli smo pregled novejše literature in študij s področja tehnologije nano-CT, s poudarkom na njegovi uporabi v biomedicinskih raziskavah ter potencialni integraciji v klinično prakso.
Rezultati: Nano-CT se je izkazal kot zelo uporabna tehnika v različnih vejah medicine, vključno s kardiologijo, vaskularno medicino, nevrologijo, pulmologijo, onkologijo in zobozdravstvom. Omogoča edinstven vpogled v arhitekturo tkiv, celične podrobnosti in patološke procese, kar bistveno izboljšuje razumevanje bolezni in podpira napredek v diagnostiki, načrtovanju zdravljenja ter novih terapevtskih strategijah.
Zaključki: Kljub izjemnemu potencialu na področju biomedicinskih raziskav je klinična uporaba nano-CT še vedno soočena z več izzivi, kot so omejitve v hitrosti slikanja, kontrastu mehkih tkiv, sevalni obremenitvi in velikosti vzorcev. Nadaljnje tehnološke inovacije, validacija s kliničnimi študijami ter razvoj multimodalnih slikovnih pristopov so nujni za uspešno integracijo nano-CT v rutinsko medicinsko diagnostiko in personalizirano medicino.
Prenosi
Literatura
1. Wang J, Fleischmann D. Improving Spatial Resolution at CT: Development, Benefits, and Pitfalls. Radiology. 2018;289(1):261-2.
2. Liu X, Chen R, Huang J, Lei Y, Yang Q, Li J. Optimization-based algorithm for x-ray super-resolution imaging. Optical Engineering. 2022;61(4):043102.
3. Sartoretti T, Landsmann A, Nakhostin D, Eberhard M, Roeren C, Mergen V, et al. Quantum Iterative Reconstruction for Abdominal Photon-counting Detector CT Improves Image Quality. Radiology. 2022;303(2):339-48.
4. Duan Y, Cheng H, Wang K, Mou X. A Novel Stationary CT Scheme Based on High-Density X-Ray Sources Device. IEEE Access. 2020;8:112910-21.
5. Langer M, Peyrin F. 3D X-ray ultra-microscopy of bone tissue. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(2):441-55.
6. Peyrin F, Dong P, Pacureanu A, Langer M. Micro- and nano-CT for the study of bone ultrastructure. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014;12(4):465-74.
7. Boca C, Truyen B, Henin L, Schulte AG, Stachniss V, De Clerck N, et al. Comparison of micro-CT imaging and histology for approximal caries detection. Scientific Reports. 2017;7(1):6680.
8. Kampschulte M, Langheinirch AC, Sender J, Litzlbauer HD, Althöhn U, Schwab JD, et al. Nano-Computed Tomography: Technique and Applications. Rofo. 2016;188(2):146-54.
9. Kalender WA. Computed tomography: Fundamentals, system technology, image quality, applications. 3 ed: Publicis MCD Verlag; 2011 2011.
10. Withers PJ. X-ray nanotomography. Mater Today. 2007;10(12):26-34.
11. Boerckel JD, Mason DE, McDermott AM, Alsberg E. Microcomputed tomography: approaches and applications in bioengineering. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(6):144-.
12. van Rietbergen B, Weinans H, Huiskes R, Odgaard A. A new method to determine trabecular bone elastic properties and loading using micromechanical finite-element models. J Biomech. 1995;28(1):69-81.
13. Metscher BD. MicroCT for developmental biology: a versatile tool for high-contrast 3D imaging at histological resolutions. Dev Dyn. 2009;238(3):632-40.
14. Schaeper JJ, Kampshoff CA, Wolf BJ, Roos L, Michanski S, Ruhwedel T, et al. 3D virtual histology of rodent and primate cochleae with multi-scale phase-contrast X-ray tomography. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):7933.
15. Walsh CL, Tafforeau P, Wagner WL, Jafree DJ, Bellier A, Werlein C, et al. Imaging intact human organs with local resolution of cellular structures using hierarchical phase-contrast tomography. Nat Methods. 2021;18(12):1532-41.
16. Khoury BM, Bigelow EM, Smith LM, Schlecht SH, Scheller EL, Andarawis-Puri N, et al. The use of nano-computed tomography to enhance musculoskeletal research. Connect Tissue Res. 2015;56(2):106-19.
17. Müller M, Kimm MA, Ferstl S, Allner S, Achterhold K, Herzen J, et al. Nucleus-specific X-ray stain for 3D virtual histology. Scientific Reports. 2018;8(1):17855.
18. Busse M, Müller M, Kimm MA, Ferstl S, Allner S, Achterhold K, et al. Three-dimensional virtual histology enabled through cytoplasm-specific X-ray stain for microscopic and nanoscopic computed tomography. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2018;115(10):2293-8.
19. Stolz E, Yeniguen M, Kreisel M, Kampschulte M, Doenges S, Sedding D, et al. Angioarchitectural changes in subacute cerebral venous thrombosis. A synchrotron-based micro- and nano-CT study. NeuroImage. 2011;54(3):1881-6.
20. Ahmed HM. Nano-computed tomography: current and future perspectives. Restor Dent Endod. 2016;41(3):236-8.
21. Tomaszewska IM, Skinningsrud B, Jarzębska A, Pękala JR, Tarasiuk J, Iwanaga J. Internal and external morphology of mandibular molars: An original micro-CT study and meta-analysis with review of implications for endodontic therapy. Clin Anat. 2018;31(6):797-811.
22. Laperre K, Depypere M, van Gastel N, Torrekens S, Moermans K, Bogaerts R, et al. Development of micro-CT protocols for in vivo follow-up of mouse bone architecture without major radiation side effects. Bone. 2011;49(4):613-22.
23. Midgley PA, Ward EP, Hungría AB, Thomas JM. Nanotomography in the chemical, biological and materials sciences. Chem Soc Rev. 2007;36(9):1477-94.
24. Erdem S, Gürbüz E, Uysal M. Micro-mechanical analysis and X-ray computed tomography quantification of damage in concrete with industrial by-products and construction waste. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2018;189:933-40.
25. Holler M, Diaz A, Guizar-Sicairos M, Karvinen P, Färm E, Härkönen E, et al. X-ray ptychographic computed tomography at 16 nm isotropic 3D resolution. Scientific Reports. 2014;4(1):3857.
26. Yu Y-S, Farmand M, Kim C, Liu Y, Grey CP, Strobridge FC, et al. Three-dimensional localization of nanoscale battery reactions using soft X-ray tomography. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):921.
27. Scharf J, Chouchane M, Finegan DP, Lu B, Redquest C, Kim M-c, et al. Bridging nano- and microscale X-ray tomography for battery research by leveraging artificial intelligence. Nature Nanotechnology. 2022;17(5):446-59.
28. Claro PIC, Borges EPBS, Schleder GR, Archilha NL, Pinto A, Carvalho M, et al. From micro- to nano- and time-resolved x-ray computed tomography: Bio-based applications, synchrotron capabilities, and data-driven processing. Applied Physics Reviews. 2023;10(2).
29. Science O, Technology SI. New metrological technique uses stress for nanotomography. Physorg. 2022.
30. Brahimetaj R, Cornelis J, Jansen B. Micro-CT Microcalcification Analysis: A Scoping Review of Current Applications and Future Potential in Breast Cancer Research. Tomography. 2024;10(11):1716-29.
31. Downey CM, Singla AK, Villemaire ML, Buie HR, Boyd SK, Jirik FR. Quantitative Ex-Vivo Micro-Computed Tomographic Imaging of Blood Vessels and Necrotic Regions within Tumors. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41685.
32. Starosolski Z, Villamizar CA, Rendon D, Paldino MJ, Milewicz DM, Ghaghada KB, et al. Ultra High-Resolution In vivo Computed Tomography Imaging of Mouse Cerebrovasculature Using a Long Circulating Blood Pool Contrast Agent. Scientific Reports. 2015;5(1):10178.
33. Mould RF. Röntgen and the discovery of X-rays. The British Journal of Radiology. 1995;68(815):1145-76.
34. Filler A. The History, Development and Impact of Computed Imaging in Neurological Diagnosis and Neurosurgery: CT, MRI, and DTI. Nature Precedings. 2009.
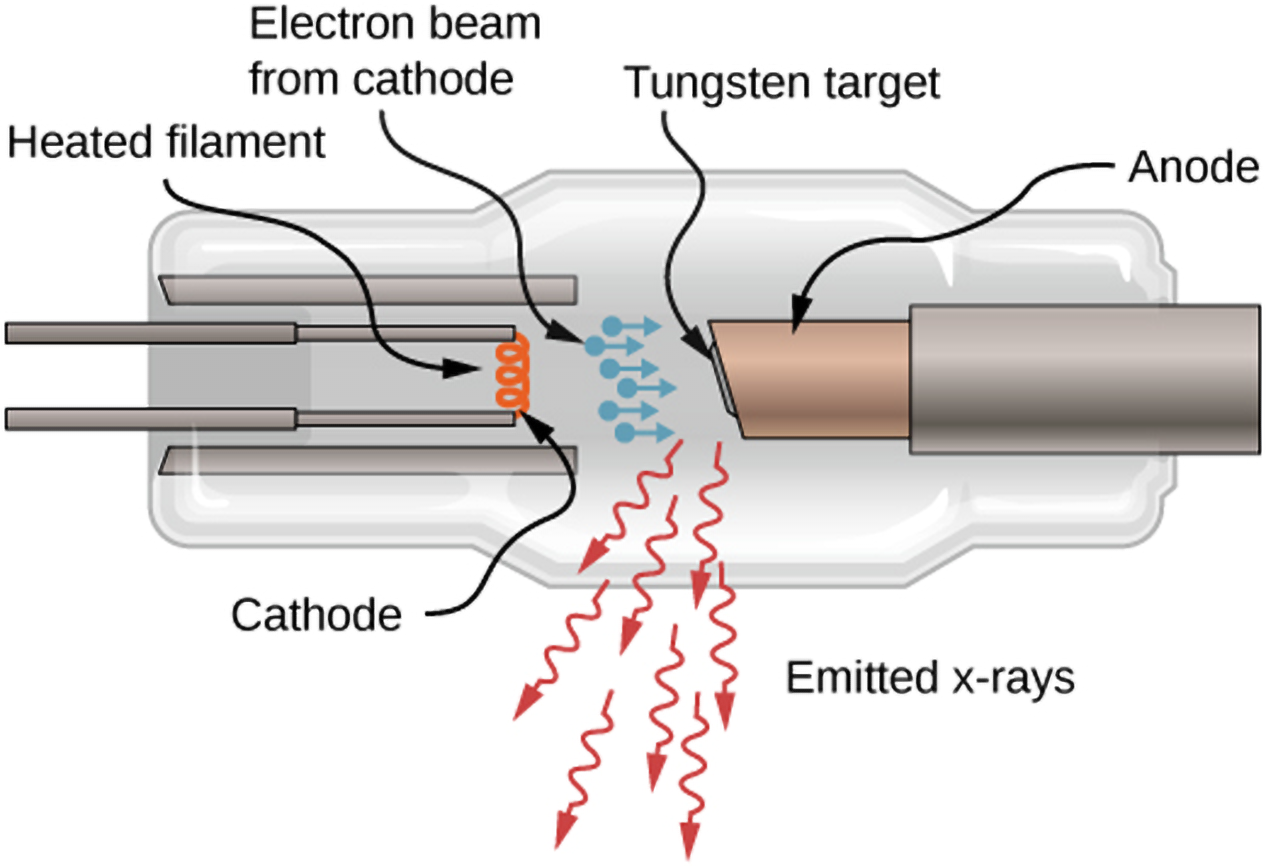
35. Seibert JA. X-Ray Imaging Physics for Nuclear Medicine Technologists. Part 1: Basic Principles of X-Ray Production. J Nucl Med Technol. 2004;32(3):139-47.
36. Bell D, Mudgal P. X-ray production. Radiopaedia org. 2013.
37. Haaga JR. CT and MRI of the Whole Body: Mosby/Elsevier; 2009.
38. Nievelstein RAJ, Quarles van Ufford HME, Kwee TC, Bierings MB, Ludwig I, Beek FJA, et al. Radiation exposure and mortality risk from CT and PET imaging of patients with malignant lymphoma. Eur Radiol. 2012;22(9):1946-54.
39. Lecchi M, Fossati P, Elisei F, Orecchia R, Lucignani G. Current concepts on imaging in radiotherapy. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 2008;35(4):821-37.
40. Kwong RY, Yucel EK. Computed Tomography Scan and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Circulation. 2003;108(15):e104-e6.
41. Shaikh Z, Torres A, Takeoka M. Neuroimaging in Pediatric Epilepsy. Brain Sci. 2019;9(8).
42. Radiation protection of patients during PET/CT scanning | IAEA 2022 [updated 2022/01/07/. Available from: https://www.iaea.org/resources/rpop/health-professionals/nuclear-medicine/pet-ct/patients.
43. Pantić M, Maver U, Rožanc J, Vihar B, Andrejč DC, Knez Ž, et al. Evaluation of ethanol-induced chitosan aerogels with human osteoblast cells. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2023;253:126694.
44. Ćurić LČ, Šuligoj M, Ibic M, Marovič N, Vihar B, Vesenjak M, et al. Development of a novel NiCu nanoparticle-loaded polysaccharide-based hydrogel for 3D printing of customizable dressings with promising cytotoxicity against melanoma cells. Materials Today Bio. 2023;22:100770.
45. Sever M, Škrinjar D, Maver T, Belak M, Zupanič F, Anžel I, et al. The Impact of Temperature and the Duration of Freezing on a Hydrogel Used for a 3D-Bioprinted In Vitro Skin Model. Biomedicines. 2024;12(9):2028.
46. Vajda J, Banović L, Miško M, Drstvenšek I, Milojević M, Maver U, et al. Algorithmic linearization improves Syringe-based extrusion in elastic systems using Hydrogel-based materials. Materials & Design. 2023;229:111884.
47. Novak N, Al-Ketan O, Mauko A, Krstulović-Opara L, Tanaka S, Borovinšek M, et al. Quasi-static and impact behaviour of polymer-metal interpenetrating phase TPMS composites. Compos Struct. 2025;366:119225.
48. Ročnik Kozmelj T, Žula M, Teržan J, Likozar B, Maver U, Činč Ćurić L, et al. Understanding stability, oligomerization and deactivation during catalytic lignin hydrodeoxygenation by mechanistic reaction micro-kinetics linked with 3D catalyst particle nanotomography. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2023;414:137701.
49. Olăreț E, Stancu I-C, Iovu H, Serafim A. Computed Tomography as a Characterization Tool for Engineered Scaffolds with Biomedical Applications. Materials. 2021;14(22):6763.
50. Dreier T, Krüger R, Bernström G, Tran-Lundmark K, Gonçalves I, Bech M. Laboratory x-ray nano-computed tomography for biomedical research. Journal of Instrumentation. 2024;19(10):P10021.
51. Li H, Pan M, Li Y, Liang H, Cui M, Zhang M, et al. Nanomedicine: The new trend and future of precision medicine for inflammatory bowel disease. Chin Med J. 2024;137(24):3073-82.
52. Burghardt AJ, Link TM, Majumdar S. High-resolution computed tomography for clinical imaging of bone microarchitecture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(8):2179-93.
53. Haugen HJ, Qasim SB, Matinlinna JP, Vallittu P, Nogueira LP. Nano-CT as tool for characterization of dental resin composites. Scientific Reports. 2020;10(1):15520.
54. Albers J, Svetlove A, Duke E. Synchrotron X-ray imaging of soft biological tissues - principles, applications and future prospects. J Cell Sci. 2024;137(20).
55. Gignac PM, Kley NJ, Clarke JA, Colbert MW, Morhardt AC, Cerio D, et al. Diffusible iodine-based contrast-enhanced computed tomography (diceCT): an emerging tool for rapid, high-resolution, 3-D imaging of metazoan soft tissues. J Anat. 2016;228(6):889-909.
56. Silva JMdSe, Zanette I, Noël PB, Cardoso MB, Kimm MA, Pfeiffer F. Three-dimensional non-destructive soft-tissue visualization with X-ray staining micro-tomography. Scientific Reports. 2015;5(1):14088.
57. Walton LA, Bradley RS, Withers PJ, Newton VL, Watson REB, Austin C, et al. Morphological Characterisation of Unstained and Intact Tissue Micro-architecture by X-ray Computed Micro- and Nano-Tomography. Scientific Reports. 2015;5(1):10074.
58. Chaurand P, Liu W, Borschneck D, Levard C, Auffan M, Paul E, et al. Multi-scale X-ray computed tomography to detect and localize metal-based nanomaterials in lung tissues of in vivo exposed mice. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):4408.
59. Cedola A, Bravin A, Bukreeva I, Fratini M, Pacureanu A, Mittone A, et al. X-Ray Phase Contrast Tomography Reveals Early Vascular Alterations and Neuronal Loss in a Multiple Sclerosis Model. Scientific Reports. 2017;7(1):5890.
60. Kavkova M, Zikmund T, Kala A, Salplachta J, Proskauer Pena SL, Kaiser J, et al. Contrast enhanced X-ray computed tomography imaging of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer disease rat model on lab based micro CT system. Scientific Reports. 2021;11(1):5999.
Prenosi
Objavljeno
Številka
Rubrika
Licenca
Avtorske pravice (c) 2025 Jernej Vajda, Marko Milojević, Uroš Maver, Boštjan Vihar (Author)

To delo je licencirano pod Creative Commons Priznanje avtorstva 4.0 mednarodno licenco.